Hard Disks :
Physically , there are four common types of hard disks ; SSD , SATA , PATA and SCSI. Any logical disk can be Basic or Dynamic .
Basic Disk :
Commonly used in hosting Operating System files. It consists of number of partitions with two styles ; MBR or GPT .
- MBR style can be primary or extended partition , but with limitation of maximum 4 primary partitions. To overcome this issue , there can be a number of logical drives (partitions) under the extended partition.
- GPT style has no limitation of partitions number.
Dynamic Disk :
used in huge storage resources . Hosting OS on it is NOT common and may lead to unexpected errors. It stores data in volumes . There are 5 types of volumes :
- Simple ~ like a normal partition
- Mirrored ~ provides a copy of a volume on another disk
- Striped ~ improves disk input/output (I/O) performance by distributing I/O requests across disks
- Spanned ~ attaching one volume with two physical disks
- RAID-5 ~ like spanned , but more than 2
This type of disks uses databases to track information about volumes and other disks.
Partition table :
records info about primary , extended and logical partitions.
FileSystem :
a method of organizing and storing data on disks in a human readable form. we may see 4 types of filesystem :
- Conventional ~ like ext2 , ext3 ,Btrfs, NTFS
- Flash storage ~ YAFFS
- Databases
- Special purposes ~ sysfs , procfs , debugfs
 linux vs. windows FS overview
linux vs. windows FS overview
Everything in Linux is a file or object like a file , even the physical devices.
One can access the existing devices from /dev directory .
Mount :
is a program that instructs the OS that user or application needs to access a certain area(ex. partition) of disk , then OS mount it in a certain space called mount points , where user can access it .
Filesystem Hierarchy Standard in Linux:
In Linux , files and directories are stored in hierarchical form starting from the root represented by ( / ) sign , ending with sub-directories and files.
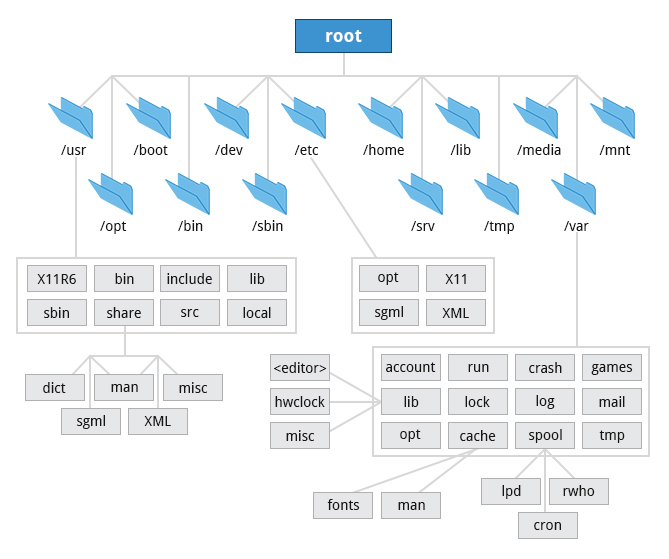
- etc ~ for configuration
- home ~ all users are allocated in this directory with their home sub-directories
- dev ~ attached devices
- boot ~ bootloader itself and its information
- tmp ~ temporary data
- bin ~ binary files for linux main tools and commands
- lib ~ important libraries
Inode table :
A fact about your photos on social media . Do you know that anyone may track your location , know your device type or even keep sensitive info about you ? That is called MetaData .
Files are stored in table with certain index and some details like :
- Owner of file ~ user or group
- File serial number
- Permissions ~ Read, Write and Execute
- Timestamps of last modifying ,changing or accessing
- Place on disk
- Size
- Number of blocks ( files are stored in something dependent on partition size called blocks )
File types in Linux :
- Normal file ~represented by (-).
- Directory ~ d (like folder in windows)
- Hard link ~ -(another name of existing file)
- Symbolic link ~ l (shortcuts)
- Socket ~ s (passes data between 2 processes)
- Named pipe ~ p (like socket ,but users can’t use it directly)
- Character device ~ c (provides unbuffered direct access to the hardware device)
- Block device ~ b (like character device ,but it always allows the programmer to read or write a block of any size of data — buffered)
Thanks!